As intense rainfall events, droughts and heat increase, the optimisation of urban water systems is becoming more and more important. The use of hydrodynamic computations and water simulations for urban drainage design, urban planning and designing and monitoring climate adaptation measures is crucial.
An improved insight into urban water systems leads to better decisions, better use and better designs.
Urban water experts and urban designers typically face these challenges:
- How to make this new urban area resilient to extreme rainfall events?
- What possibilities do we have to include climate adaptation measures in this existing dense urban area?
- How can we involve other stakeholders and support other experts in the design of a water proof city?
Our users choose 3Di for hydrodynamic computations to solve these challenges for the following 10 reasons.
Fast & Accurate
Integral
Visual Results

1.Integral computations for all domains (0D-1D-2D)
Traditionally, urban drainage design has been performed for relatively small rainfall events. In most cases, current sewerage systems are not equipped to cope with large rainfall events. With 3Di, we acknowledge that climate adaptation measures need to be taken both above and underground. That’s why the computational core is built in such a way that it can handle large areas with high resolution above ground, and include sewerage systems, groundwater, and surface water if needed. The exchange between these systems is fast and accurate, ensuring that investments in urban drainage design are effective.
A common trend is to convert impervious surfaces into rain gardens or other types of sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDs) or Nature-Based Solutions (NBS). With the integral computations in 3Di, we ensure that the effects of these solutions are computed in the most accurate way possible.

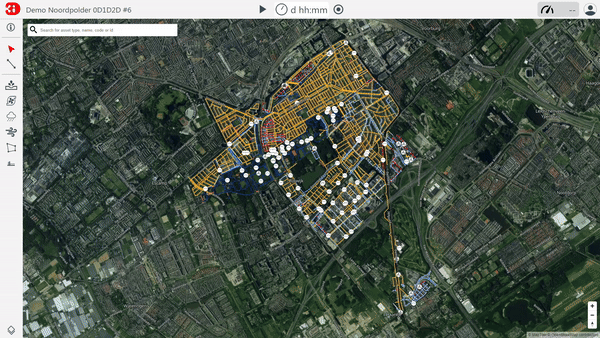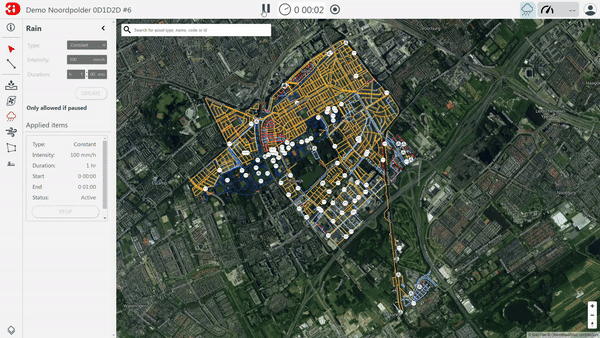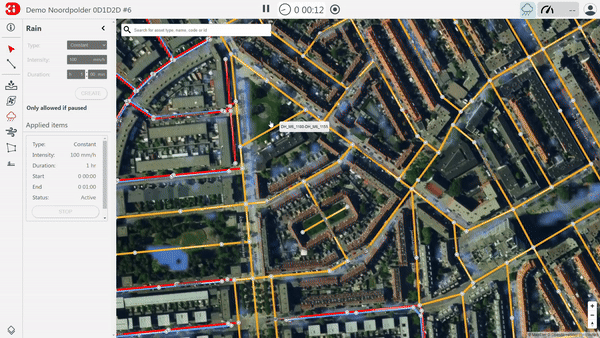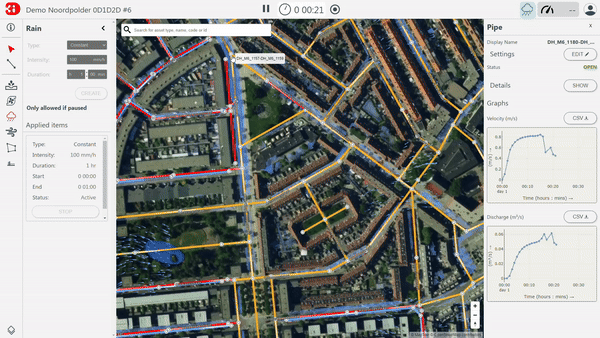
2. Stakeholder involvement
3Di Live is tailored for stakeholder involvement. It serves as the online user interface for running and using the model developed for hydrodynamic analysis. This interface is simple, allowing multiple users to operate the model. To use it, a web browser (preferably Google Chrome) and an internet connection are the only technical requirements. The computations run in the cloud, so even if your internet connection is disrupted, the computation continues.
Within the user interface, you can experiment with the model. You can ‘throw’ different forcings (such as rains, discharges, pumps) at the model to see their impact. Additionally, you can interact with the model, for example by placing a mobile barrier or by altering the elevation to see the effect when you elevate the surface or, for instance, dig a retention pond.
3Di Live is often used to demonstrate how the water system works, to perform preliminary ‘what-if’ analyses, and to ‘optioneer’ possible solutions to mitigate the consequences of floods. It bridges the gap between water experts and non-water experts.
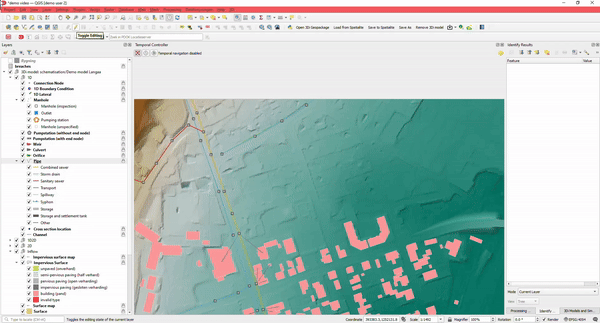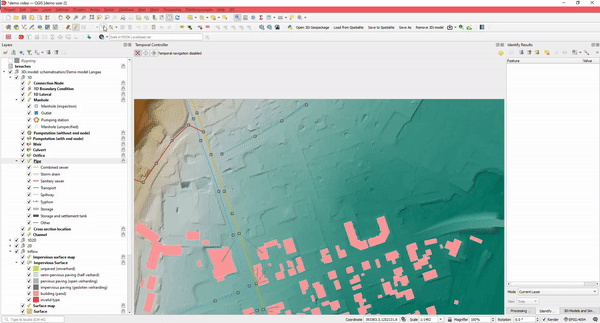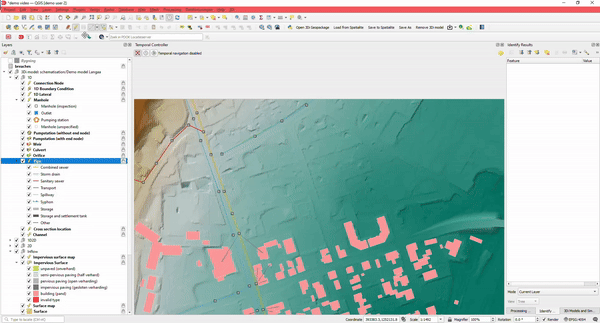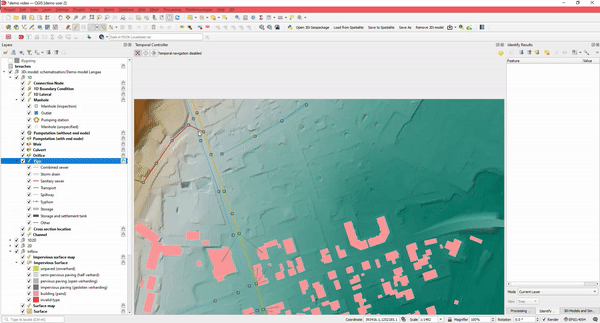
3. Easy to use: Editing
Using the Modeller Interface, you have both the power of QGIS and a variety of specialized processing tools available. Import from different GIS datasets or existing urban models into the 3Di database using our specialized importer.
There are special tools that assist the user in editing. For example, when drawing a pipe, manholes and connection nodes are automatically added and supplied with sensible default values, ensuring you can start simulating quickly.
Quickly connect your buildings (DWF) to connection nodes, draw rain gardens, or other types of SUDs using the Raster editing tools.
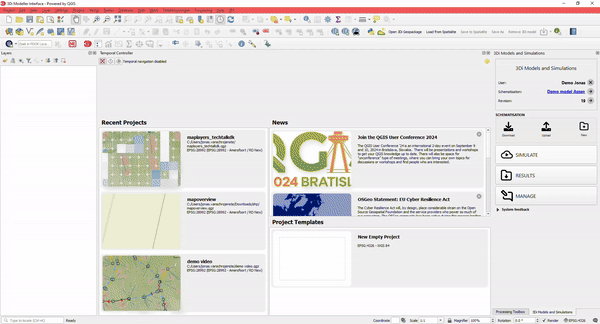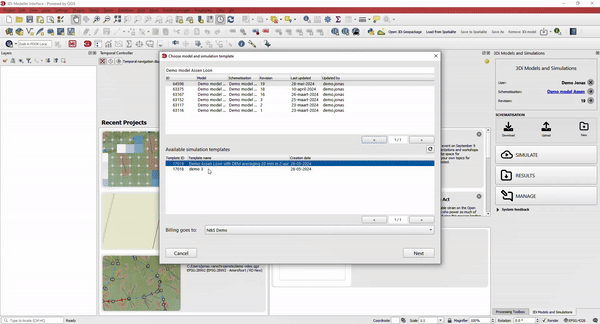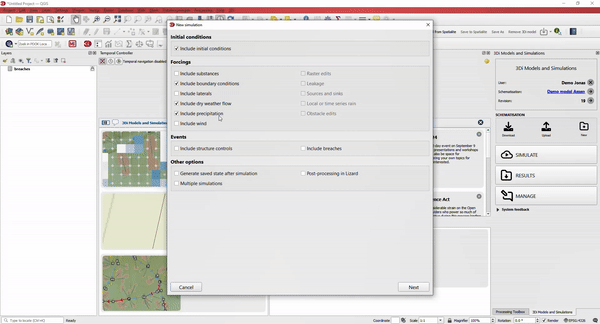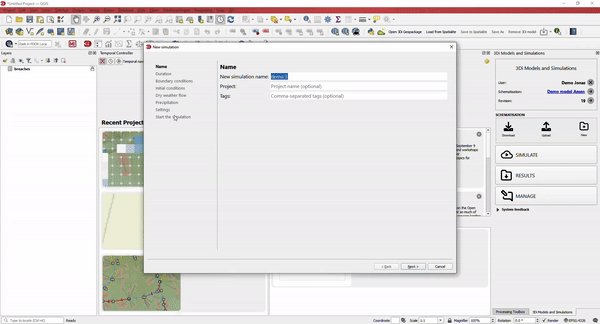
4. Easy to use: Run simulation using the Wizard
Run simulations using the Simulation Wizard in the Modeller Interface. The Simulation Wizard assists you in selecting the settings for your simulation, including boundary conditions and initial water levels.
Every model can have several simulation templates containing information on rainfall events. By storing all settings in a simulation template, simulations can be re-run at a later stage with the exact same input.
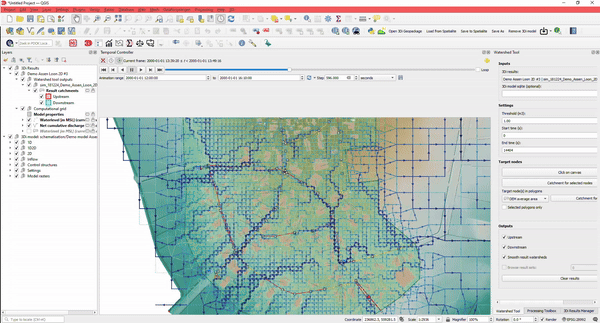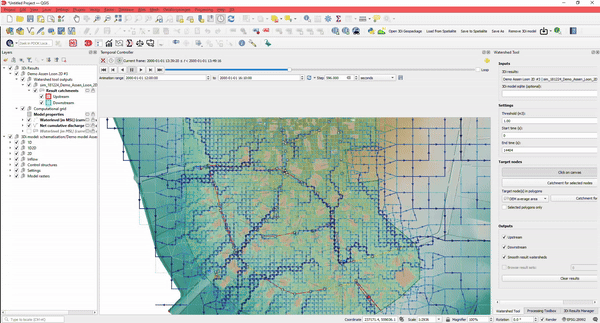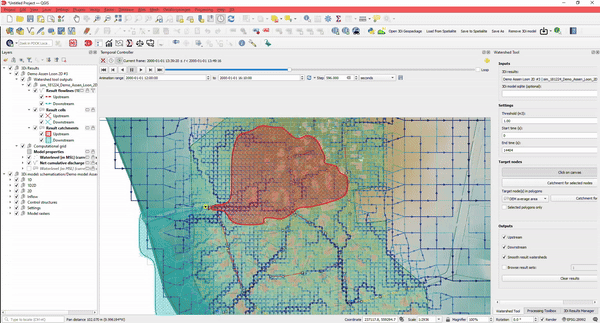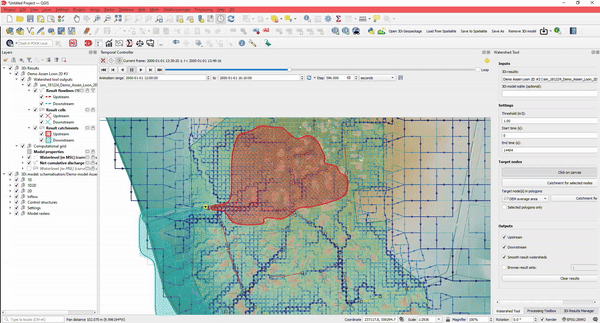
5. Easy to use: Analysing Results
Analysing results of schematisations can be done in many different ways. Of course, you can:
- Create sideview profiles
- Get water levels for nodes
- Determine watersheds for any point in your simulation. Where is the water at this location coming from?
- Determine how much water is coming from which direction
And the best part: you can do this without the need to rerun your simulation.
This, together with lots of styling options, makes it a versatile instrument suitable for any urban design challenge involving water.
6. Using a Major Advantage of Cloud Computing: Versioning and Online Collaboration
3Di facilitates hydrodynamic simulations in the cloud. Simply use a standard laptop to run the most advanced simulations, or even multiple simulations simultaneously; the cloud makes it possible.
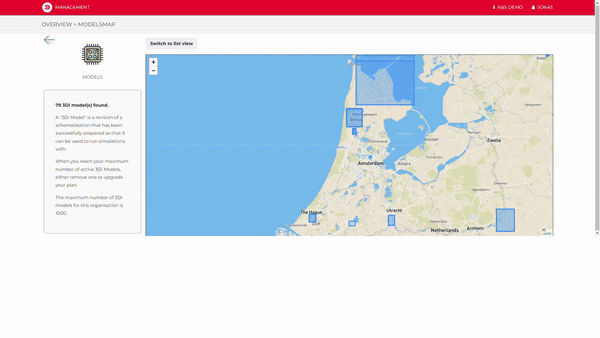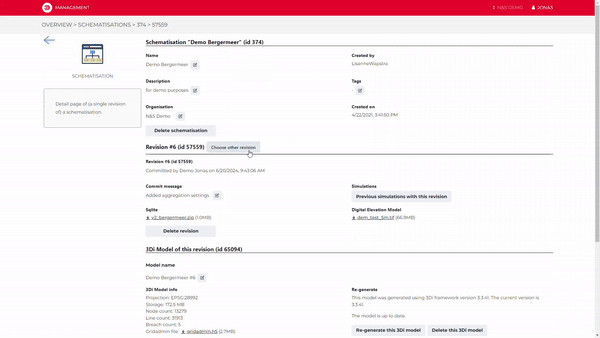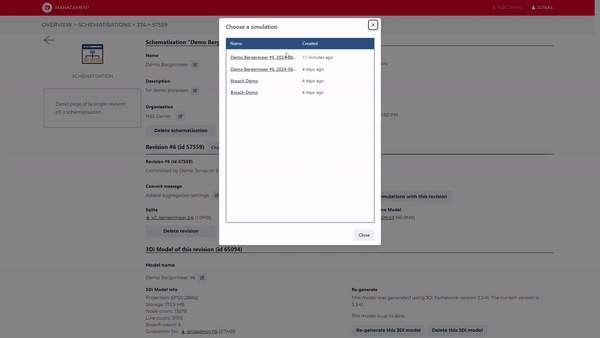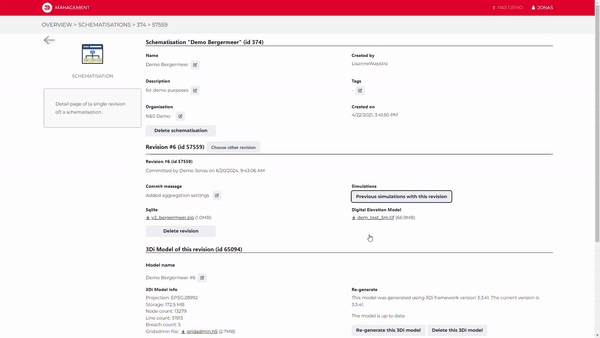
When uploading a new version of your schematisation to the cloud, 3Di automatically provides versioning for your schematisations and models.
Store your work in the cloud, and collaborate with your colleagues and/or clients to tackle your urban design challenges.
7. Fully customizable
3Di is fully customisable to meet your needs. You can change the language of the interface and style the maps in your preferred way.
Most importantly, because every part of 3Di is accessible using an API, thanks to its API-by-design policy, everything — and we mean everything — is accessible via scripts. From automated model creation to mass simulations, to model checking, validating, and calibrating, you can use Python or SQL.
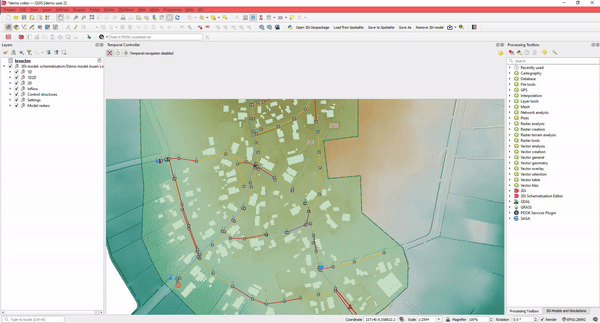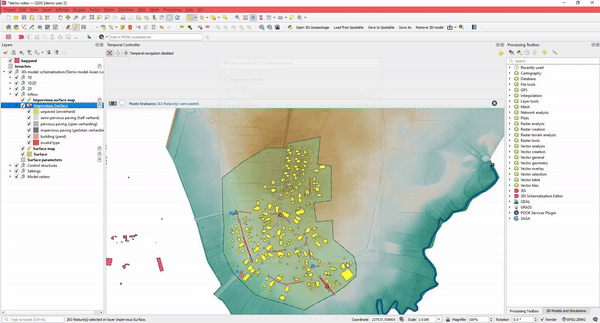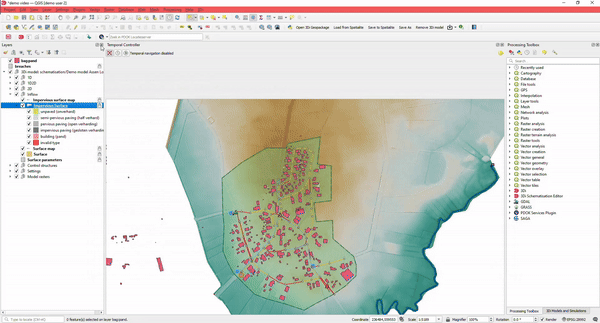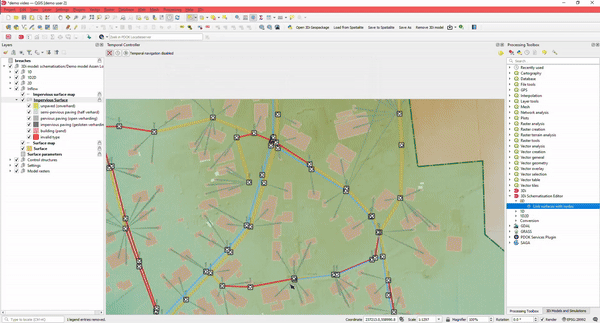
8. Integrate 3Di with Your Most Used Datasets
3Di can be fully integrated with standard GIS datasets.
When building schematisations, you can import open datasets, convert them to 3Di schematisations, or use open data DEM files.
We organised a webinar in which we demonstrate how to build a fully working 1D-2D urban model within 15 minutes: watch here.
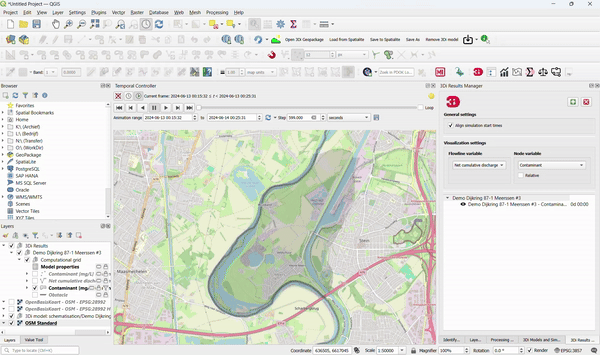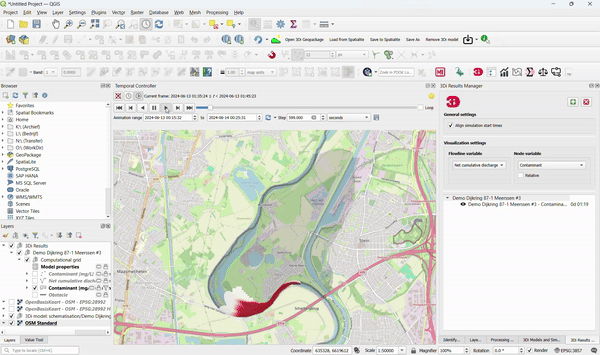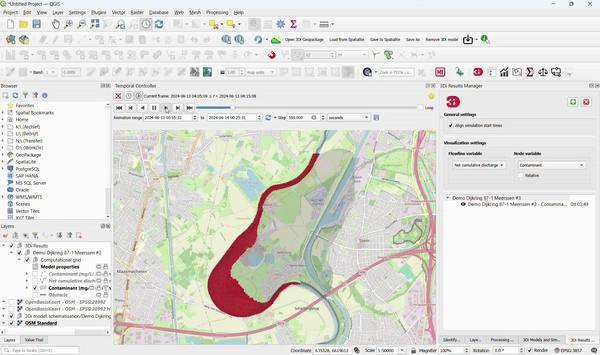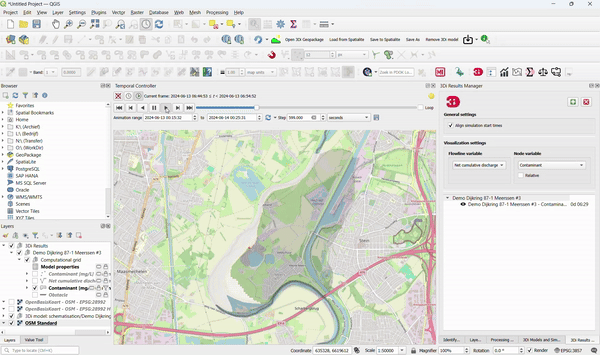
9. Use 3Di Computations for Better Insight into Water Quality
3Di models can be used to:
- Track substances through all domains.
- Compute residence time.
- Show the origin of water in a simulation. To accomplish this, no adjustments to existing 3Di models are required!
Specific applications in urban areas include:
- Showing where the overflow water ends up.
- Computing the composition of water during dry weather flow, rain, and inflow from open water.
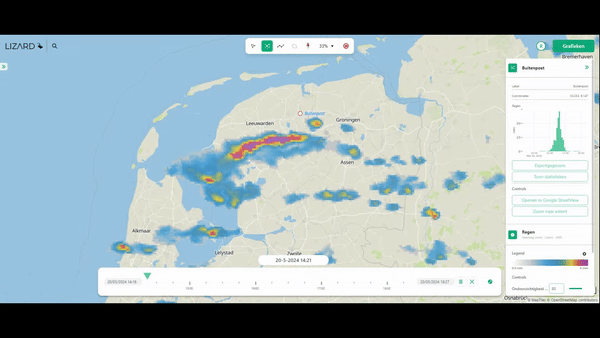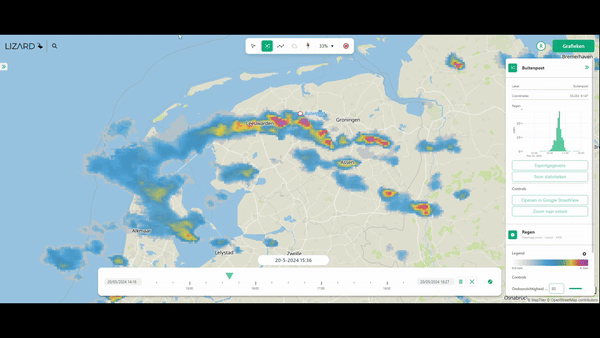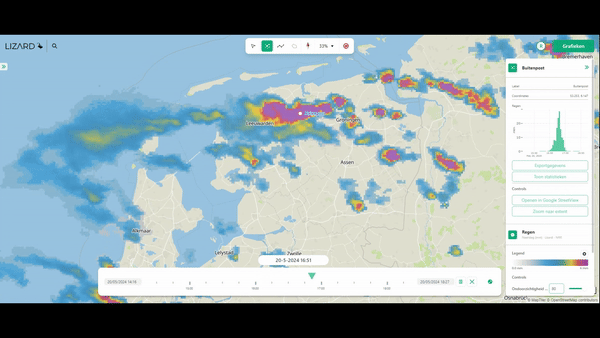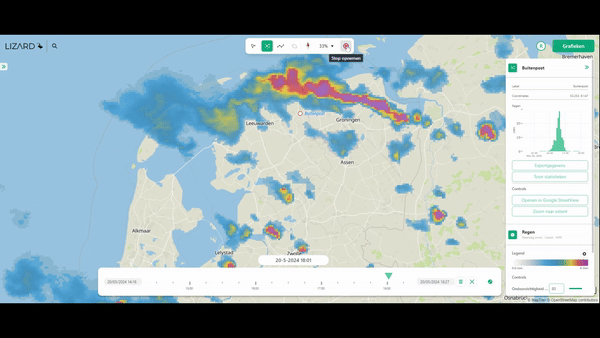
10. Compute the Impacts of Different Types of Rainfall
With 3Di, it is possible to use different types of rainfall events:
- Design rainfall.
- Timeseries, uniform across the model.
- Rainfall simulations (imported from Rainfall Radar, or forecasts), varying in space and time.
The best aspect is the way 3Di handles the rain-on-grid method. Rainfall can enter the model either via the roofs of buildings on so-called 0D surfaces, but by default, it enters the model via rain on grid. This ensures that the most realistic simulations are possible.